Created in 2009, Bitcoin has generated unprecedented interest this year, leaving many wondering:
- What is Bitcoin?
- What do I need to know about it and other cryptocurrencies?
- Should I buy it?
What exactly is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is simply a form of digital money. But it is also a ledger, a network, and a whole new way of thinking about transactions. But there's much more to Bitcoin than that. Read on:

Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency. This means that the currency and its transactions are protected and powered by encryption, much like the technology relied on to secure everything from online bank accounts to Pentagon military secrets. This makes Bitcoin transactions second only to cash for their privacy.
Bitcoin is decentralized. Nearly every country in the world relies on a central bank to print money according to its judgment of what is best for the nation's economy. Unfortunately, history offers many examples where this centralization of power had disastrous consequences, notably the devastating hyperinflation of the German Mark in the 1920s, and more recently, the now worthless Zimbabwe dollar (Zimbabwe's recent crises has sent demand for Bitcoin surging).
Bitcoin is the exact opposite. As a peer-to-peer network, it relies on countless "nodes" — participating computers running the Bitcoin code — to process and verify all Bitcoin transactions, rather than one central governing body. This is called a distributed data structure, and it prevents meddling from inside or outside malicious forces. How can we be sure? Because...

Bitcoin is open source technology. "Open source" means that the code in use is completely transparent, meaning that anyone in the world can review it for vulnerabilities, and all participating computers/nodes must adopt it to facilitate transactions. Does open source mean that your transactions are public? Just the opposite...

Bitcoin is (mostly) private. As more of our data has moved online, identity theft has become an increasing problem, as the monumental Equifax hack demonstrated.
One solution to our privacy concerns is simply to expose less personal information. According to Investopedia, "a typical Visa transaction involves four parties: the merchant, the [merchant's payment processor], the [card holder's bank], and the individual cardholder."
By contrast, a Bitcoin transaction only relies on an alphanumeric "key" that applies only to that transaction, virtually eliminating the threat of identity theft. Speaking of which...

Bitcoin is secure. The real genius of Bitcoin is the technology behind it, called blockchain.
We'll describe blockchain in detail below, but it essentially it allows for every participating "node" in the Bitcoin network to verify your transaction. Because of this multi-part verification, it makes it almost impossible for any party to falsify a transaction. As the security measures for Bitcoin "wallets" become more advanced, your currency is at least as safe as your online bank account, without the attendant costs and fees. Speaking of fees...

Bitcoin is efficient. So far, no financial institution has succeeded in developing a transaction system that doesn't rely heavily on a third party arbiter to ensure neither party reneges on their part of the deal. We can blame this basic conundrum for virtually all of the fees we face when pulling out our credit cards or initiating a wire transfer.
By its very design, Bitcoin, reduces this hurdle to a hitherto inconceivably small (and cheap) size. And that's because...

Bitcoin is "trustless". Right now, the transactions you make with everyone from your corner store to your online bank are predicated on trust that both parties in the transaction will hold up their side of the deal. But what if you could completely remove trust from the equation, and have 100% confidence that your transaction would be successful? Because every Bitcoin "node" is processing and verifying your transaction, it means neither party can manipulate the system.
Blockchain and the "double spend" problem
Digital money is more complicated than paper money. What stops someone from endlessly duplicating their digital money, or adding a few zeros to their savings? This is known as the double-spend problem, and blockchain does an elegant job of solving it. Here's MIT Assistant Professor and cryptocurrency expert Christian Catalini describing how it works:
A decentralized network of volunteer-run nodes ... vote on the order in which transactions occur ... The network's algorithm ensures that each transaction is unique … Once a majority of nodes reaches consensus that all transactions in the recent past are unique (that is, not double spent), they are cryptographically sealed into a block.
That's it — Bitcoin is run and secured by these blocks, which together form a kind of chain, Hence blockchain. Again, Professor Catalani:
Copies exist and are simultaneously updated with every fully participating node in the ecosystem….Every node that participates in the network can verify the true state of the ledger and transact on it at a very low cost.
In this way, everyone ensures everyone else is playing fair. It's built into the very heart of Bitcoin.
Can it really work?
At this point, few credible sources argue that Bitcoin (and the blockchain underneath it) is unsafe, insecure, or an inefficient way of making transactions. Rather, the big question is: can it scale into the widely adopted, borderless currency which its founders envisioned?
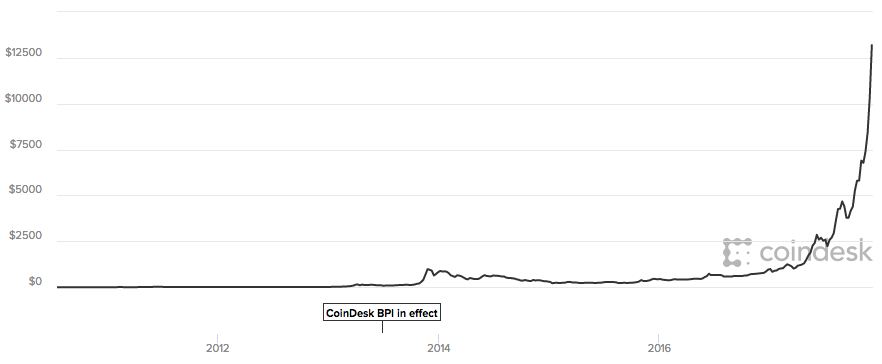
Let's take a more longitudinal view. Since its founding in 2009, Bitcoin has had a remarkable rise:
Which brings us to the very heart of what makes currencies useful in the first place — widespread adoption. And on that matter, only time will tell.
In a nutshell
The benefits:
- Decentralized.
- Open source.
- Private.
- Secure.
- Trustless.
- Efficient.
The risks:
- Adoption (not guaranteed)
- Regulation (not developed)
What's next?
The real question for Bitcoin's future, besides adoption, is regulation. Spokespeople for some major US financial institutions, such as JPMorgan CEO Jamie Dimon, have expressed skepticism. Other financial institutions like Goldman Sachs are openly mulling how to implement Bitcoin trading into their organization. Fidelity Investments has gone even further, partnering with Coinbase to allow customers to monitor their cryptocurrency position within their Fidelity accounts. Universally, banks and financial institutions appear to be enthralled with the blockchain concept underlying Bitcoin, even if outwardly expressing skepticism about the currency itself.
Bitcoin and SafeDinar.com
As of now, SafeDinar.com does not exchange Bitcoin. Interested in being notified if that ever changes? Join our Bitcoin mailing list for all updates.
Want to learn more about Bitcoin or have general Bitcoin questions? Submit them on the right in the Ask A Question section and we'll answer them in our Money Talks.